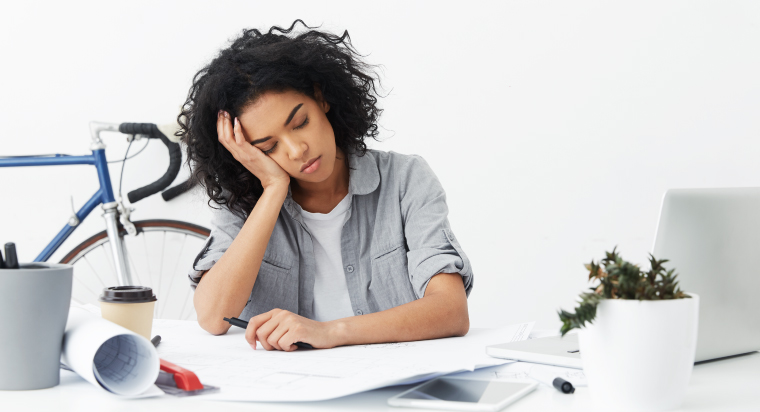
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that disrupts the body’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. Despite its relatively low prevalence, narcolepsy can have profound effects on an individual’s daily life and overall well-being.
Narcolepsy can disrupt a person’s daily life by causing excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden and uncontrollable sleep episodes, as well as impacting mood, cognitive function, and overall psychological well-being. In this article, we will address the condition, providing a deep understanding of its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, the impact on the body, the available treatment options for narcolepsy, and how to manage narcolepsy.
Understanding Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is a complex disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep, and disruptions in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. These REM episodes often involve vivid and immersive dreams, which can lead to emotional and psychological challenges. While the exact cause of narcolepsy is not fully understood, a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental triggers is believed to contribute to its development.
Symptoms of Narcolepsy
To understand how to manage narcolepsy, you need to know how to identify the condition. Here are the symptoms of the condition:
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness (EDS)
Individuals with narcolepsy struggle with overwhelming daytime sleepiness, irrespective of the amount of sleep they get at night. This unrelenting fatigue can impact daily functioning, hinder productivity, and strain relationships. - Cataplexy
Cataplexy is a distinctive symptom of narcolepsy characterized by the sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions. This can range from mild muscle weakness to complete muscle collapse, often lasting for brief moments. - Sleep Paralysis
Sleep paralysis occurs during the transitions between wakefulness and sleep. People with narcolepsy may experience a temporary inability to move or speak during this phase, which can be accompanied by vivid hallucinations. - Hallucinations
These hallucinations may occur during the onset of sleep (hypnagogic) or while waking up (hypnopompic). They can be visually or audibly intense, contributing to the unsettling nature of narcolepsy. - Disrupted Nighttime Sleep
Frequent awakenings during the night contribute to sleep fragmentation, causing further daytime sleepiness and affecting overall sleep quality.
How Narcolepsy Affects the Body
Narcolepsy’s impact extends far beyond daytime sleepiness. The disruptions in REM sleep can affect mood, cognitive function, and psychological well-being. The inability to regulate sleep patterns can result in irregular sleep schedules, making it challenging to maintain normal activities.
The sudden onset of symptoms, such as cataplexy or sleep attacks, can pose safety risks and complicate daily routines. Moreover, the unpredictability of narcolepsy’s symptoms can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and isolation.
Individuals with narcolepsy often encounter emotional struggles as well. The disorder’s impact on relationships, social interactions, and work performance can contribute to feelings of low self-esteem and reduced quality of life. The importance of addressing the emotional and psychological aspects alongside the physical symptoms is integral to achieving comprehensive well-being.
How is Narcolepsy Diagnosed?
Diagnosing narcolepsy requires a comprehensive approach that involves a thorough medical history, clinical evaluation, and sleep studies. Multiple sleep latency tests (MSLT) is commonly employed to assess sleep patterns and gauge the severity of daytime sleepiness. These tests not only aid in confirming a diagnosis but also help differentiate narcolepsy from other sleep-related disorders.
What are the Available Treatment Options?
While a cure for narcolepsy is yet to be discovered, there are several strategies available to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. Treatment plans are individualized based on the specific symptoms and needs of each patient. Common approaches include:
I. Stimulant Medications
Some prescription stimulants such as modafinil and armodafinil are effective in combatting daytime sleepiness and promoting wakefulness. Do not take any medication without being prescribed by a qualified medical professional.
II. Antidepressants
Certain antidepressants can also help manage cataplexy and other symptoms by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain.
III. Lifestyle Adjustments
Adhering to healthy sleep hygiene practices, like maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding caffeine before bedtime, can contribute to better sleep quality.
IV. Behavioral Therapies
Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can help individuals establish healthier sleep patterns and manage sleep-related anxieties.
How to Manage Narcolepsy
There are strategies individuals can adopt to effectively manage the challenges posed by narcolepsy and enhance their overall well-being. Some of them include:
1. Schedule Daytime Naps
Strategically planned short naps can provide much-needed relief from daytime sleepiness. Setting aside dedicated times for naps can help manage fatigue and maintain better alertness throughout the day.
2. Engage in Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can help boost energy levels and improve overall mood. However, it’s essential to avoid vigorous exercise close to bedtime, as it might interfere with sleep.
3. Develop Proper Stress Management Techniques
Implement stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises. Managing stress effectively can contribute to better sleep quality and emotional well-being.
4. Create a Supportive Environment
Educate family members, friends, and colleagues about narcolepsy to foster understanding and empathy. Building a supportive network can provide emotional backing and alleviate feelings of isolation.
5. Make Occupational Adjustments if Necessary
For individuals in work or educational settings, you might want to consider flexible schedules, remote work options, or accommodations that can help manage narcolepsy-related challenges.
6. Practice Self Monitoring and Care
Keep a sleep diary to track sleep patterns, symptom severity, and potential triggers. Regularly evaluating progress and adapting strategies based on personal observations can help you optimize symptom management.
7. Seek Medical Assistance
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor treatment efficacy, adjust medications if needed, and ensure overall health and well-being.
Last Words
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder that has a profound impact on an individual’s life. However, understanding its symptoms and essential steps to manage the condition can be truly helpful. If you suspect you or someone you know may be grappling with narcolepsy, seeking medical evaluation and professional guidance is crucial to obtaining an accurate diagnosis and designing a personalized treatment plan.
At the Pulmonary Clinic of the Carolinas, our expert team is dedicated to offering comprehensive care and support to individuals managing narcolepsy, empowering them to regain control over their sleep and their lives. Schedule a consultation with us today to get started!


 Translate
Translate