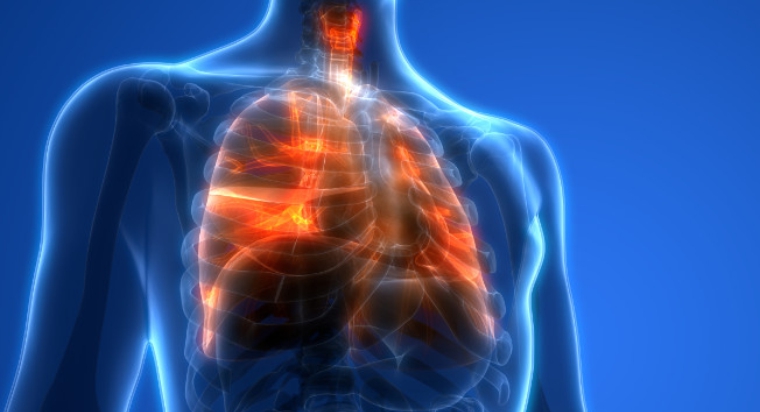
Pulmonary disease refers to any disease that affects the lungs, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung cancer, and pneumonia. Smoking is a major risk factor for many pulmonary diseases. In fact, smoking is responsible for up to 90% of all cases of lung cancer and is a major cause of COPD.
In this article, we will explore the link between smoking and pulmonary disease, explain why you should quit smoking, and provide detailed information on how to quit smoking.
Why You Should Quit Smoking
Smoking is a harmful habit that has been linked to a number of health problems, including pulmonary disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the delicate tissues of the lungs and cause inflammation. This inflammation can lead to the development of chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other forms of pulmonary disease.
Smoking also weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections like pneumonia. Here are some additional reasons why you should quit smoking:
- Improved lung function: Quitting smoking can improve lung function and reduce the risk of developing pulmonary disease.
- Reduced risk of cancer: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of lung cancer and other types of cancer.
- Improved heart health: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting smoking can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Improved overall health: Quitting smoking can improve overall health and quality of life, leading to more energy, better sleep, and improved mood.
The Link Between Smoking and COPD
COPD is a chronic respiratory disease that is characterized by difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, with up to 75% of all cases attributed to smoking.
The longer a person smokes, the greater their risk of developing COPD. However, quitting smoking at any age can reduce the risk of developing COPD and slow the progression of the disease.
The Link Between Smoking and Lung Cancer
If you’re wondering how smoking contributes to lung disease, then first, you must understand that lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Smoking is responsible for up to 90% of all cases of lung cancer.
The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the DNA in lung cells, leading to mutations that can cause cancer. The risk of lung cancer increases with the number of cigarettes smoked per day and the number of years a person has smoked.
The Link Between Smoking and Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or other organisms. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections like pneumonia.
Smokers are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia and are more likely to have severe complications from the infection. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of pneumonia and improve overall lung function.
How to Quit Smoking
Now that you have learned about the link between smoking and pulmonary disease, how can you quit smoking? Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the risk of pulmonary disease and improve overall health. Here are some tips to help you quit smoking:
1. Set a quit date
Choose a date to quit smoking and stick to it. Tell your friends and family about your quit date to get support.
2. Identify triggers
Figure out what triggers your urge to smoke and try to avoid those situations. For example, if you tend to smoke after meals, try going for a walk instead.
3. Use nicotine replacement therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy can help reduce the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal and make it easier to quit smoking. Options include nicotine gum, patches, lozenges, inhalers, and nasal sprays.
4. Seek support
Talk to your doctor, join a support group, or seek help from a quitline or counselor. Having support can make it easier to quit smoking and increase your chances of success.
5. Make lifestyle changes
Changing your routine can help break the habit of smoking. Try exercising, eating healthy, or finding new hobbies to distract yourself from the urge to smoke.
6. Avoid alcohol and caffeine
Alcohol and caffeine can trigger the urge to smoke, so it’s best to avoid them while quitting smoking.
7. Stay positive
Quitting smoking is not easy, but it’s important to stay positive and motivated. Focus on the benefits of quitting, such as improved lung function and better overall health.
Conclusion
Smoking is a major risk factor for many pulmonary diseases, including COPD, lung cancer, and pneumonia. Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the risk of these diseases and improve overall health.
By setting a quit date, identifying triggers, using nicotine replacement therapy, seeking support, making lifestyle changes, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and staying positive, you can successfully quit smoking.
Remember, quitting smoking is not easy, but it is worth it. By quitting smoking, you can improve lung function, reduce the risk of cancer and other health problems, and improve overall quality of life. Take the first step towards a healthier future by quitting smoking today.
If you are a smoker and want to quit, talk to your doctor or a smoking cessation counselor today. With the right support and resources, you can successfully quit smoking and improve your health.


 Translate
Translate