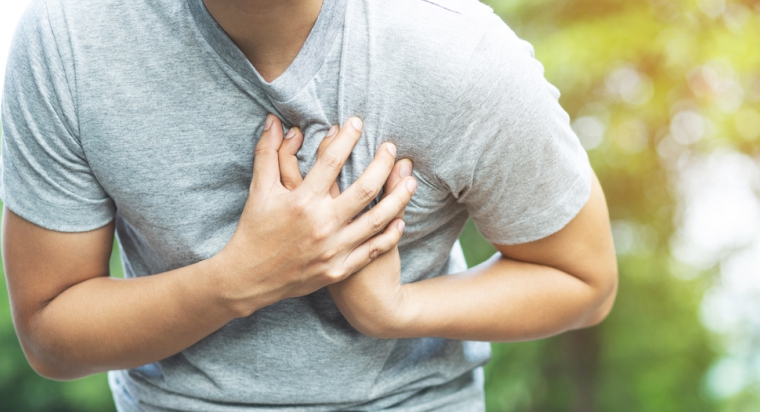
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting a type of white blood cell called CD4+ T cells. This can lead to the development of AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 2019 there were approximately 38,000 new HIV diagnoses in the United States. As of 2020, an estimated 14% of the approximately 1.2 million people living with HIV in the United States were unaware of their infection.
One of the many systems of the body that can be affected by HIV is the lungs. This is because the virus can lead to inflammation and infection in the respiratory system. It is important to keep a close eye on lung health with HIV as this can lead to severe complications. Also, understanding the connection between HIV and lung health is crucial to proactively manage any potential issues.
Some of the things to note about HIV and lung-related complications that can occur in people living with HIV include:
- Higher risk of developing pneumonia
People with HIV are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia, which is an infection of the lungs that causes inflammation and fluid buildup. This can lead to difficulty breathing, chest pain, and fever. Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of different types of bacteria and viruses, but in people living with HIV, it is most commonly caused by a bacteria called Pneumocystis jirovecii. People with HIV may be more susceptible to certain types of pneumonia, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) pneumonia.
Additionally, as a person living with HIV, your body may have a harder time fighting off the infection, which can lead to more prolonged illness and a higher risk of complications. Also, it can be more severe and harder to treat due to a weakened immune system. To prevent pneumonia, you should practice good respiratory hygiene, such as covering your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze and washing your hands frequently. Vaccines such as Pneumococcal and Flu vaccines can also help to prevent pneumonia.
2. Tuberculosis (TB) Infection
People living with HIV are also at a higher risk of developing tuberculosis (TB), a serious bacterial infection that affects the lungs. According to the World Health Organization, people living with HIV are 26 to 31 times more likely to develop tuberculosis (TB) than those without HIV. In 2019, around 38 million people were living with HIV, and of those, 1.4 million died from TB. Additionally, TB is the leading cause of death among people living with HIV, accounting for about one in three HIV-related deaths. This is because TB infection can worsen the progression of HIV, leading to a decline in the person’s overall health. This shows the importance of TB prevention, early diagnosis, and treatment among people living with HIV.
To prevent further damage and to reduce the risk of death, it is important to be tested for TB regularly and to receive appropriate treatment as soon as possible if you develop TB in the lungs.
3. Inflammation of the Bronchial tubes
Bronchitis is a condition that causes inflammation in the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to and from your lungs. If you are living with HIV, it’s important to be aware of the symptoms of bronchitis, such as a persistent cough, mucus production, and difficulty breathing. This is because, in people with HIV, bronchitis can be more severe, and persistent and lead to chronic bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a persistent cough and mucus production, which can result in difficulty breathing and reduced lung function. In people living with HIV, chronic bronchitis is more likely to occur and can be more severe due to a weakened immune system caused by the virus. The treatment for bronchitis in people living with HIV includes antibiotics, bronchodilators, and steroids to reduce inflammation and improve lung function. In some cases, especially for chronic bronchitis, quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to lung irritants, and using inhaled medications may also be recommended.
It’s important to remember the importance of regular check-ups for HIV and lung health. By being aware of the symptoms of bronchitis and seeking prompt medical attention, you can prevent the condition from becoming more severe and improve your overall lung health.
4. Increased risk of lung cancer
As a person living with HIV, it’s important to be aware of the increased risk of developing lung cancer, especially if you have a history of smoking. The weakened immune system caused by HIV can make it harder for the body to fight off cancer cells. Regular monitoring of your lung health is crucial to detect any issues early on.
In the early stages of lung cancer, there may be no noticeable symptoms, but as cancer progresses, you may experience unexplainable fatigue, persistent cough, or coughing up. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms, as prompt treatment is key to managing lung cancer effectively. So, it’s essential to keep a close watch on your lung health if you have HIV and make sure to attend regular check-ups.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, HIV can impact the lungs in a number of ways, including pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer, and bronchitis. It’s important to be aware of the potential complications and to take steps to prevent and treat them. If you have been diagnosed with HIV and have symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, or difficulty breathing, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider right away.
Take Charge of Your Lung Health Today! As someone living with HIV, it’s crucial to prioritize your lung health by getting regular check-ups and promptly treating any infections. Don’t wait – make your health a top priority now. Reach out to us today and experience exceptional medical care.


 Translate
Translate